Submitted by admin on Sat, 09/20/2008 - 21:10
Clinical Signs:
follicular hyperplasia
Morphologic diagnosis:
Skin, leg: Severe multifocal to locally extensive nodular follicular epidermal hyperplasia with dermatitis
Clinical description:
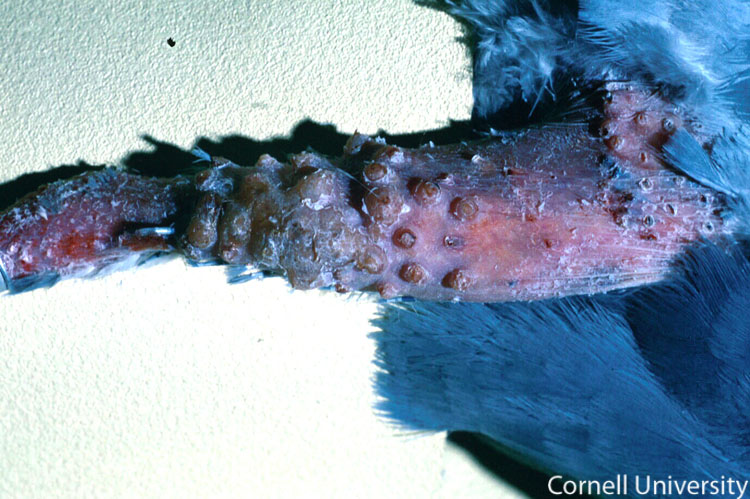
In this photograph, an advanced stage of the cutaneous (dry) form of avian pox is illustrated. Pox virus is slow-spreading and skin lesions change over a period of several weeks. Lesions progress from nodules, to small white foci, papules, vesicles, scabs, and eventually scars. In this photo, the lesions are beginning to coalesce into rough brown scabs. At this stage, if the scabs are disrupted, as seen on this distal limb, a seropurulent exudate may be observed.
Pathologic description:
The skin and leg are disrupted by multiple well-demarcated raised round nodules. At the distal aspect of the leg, these nodules coalesce to form a confluent, raised, irregularly-shaped, brown scab. Because the individual lesions are regular in shape, size, and distribution, it is likely that they correspond to a normal anatomic structure. In this case, they correspond to the feather follicles.
Record number:
7635
Case number:
Unknown
Clinical form:
Unknown
Infection type:
Unknown
Housing/mgmnt type:
Select One
Priority:
1
Rights:
© Cornell University
Image source URL:
http://cidc.library.cornell.edu/vet_avian/images/POX Adjusted/POX-012A.jpg
Etiology:
Exam findings:
Tissues and organs:
Asset type:
Species:
Image: